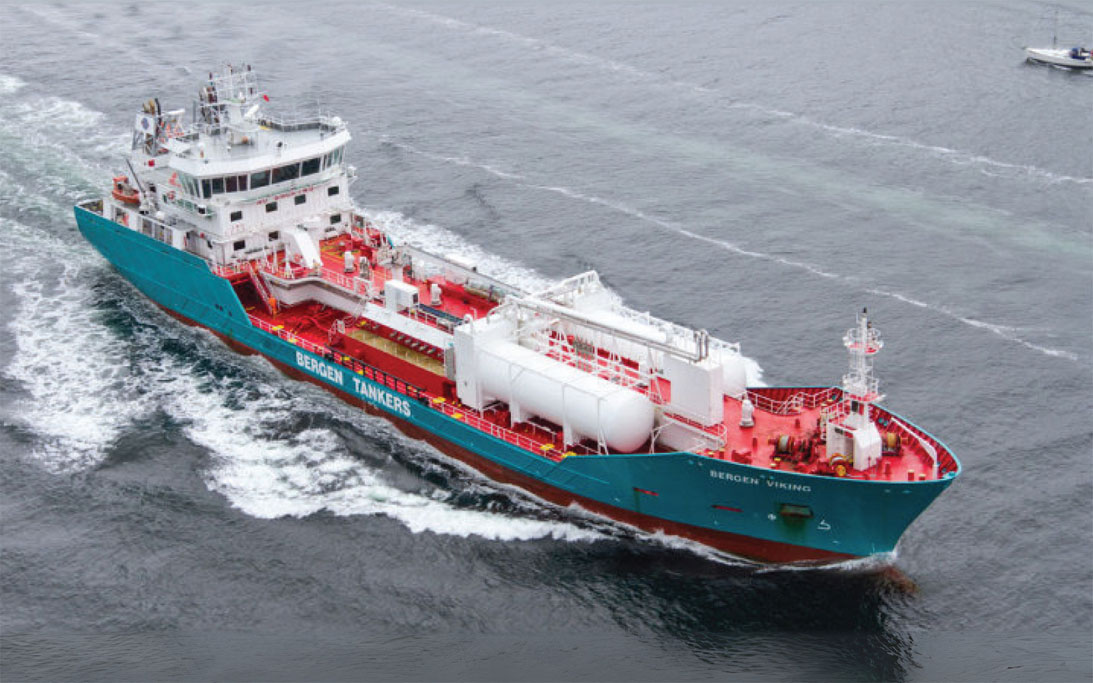
The maritime industry is undergoing a significant transformation as it seeks to reduce its carbon footprint and comply with stricter environmental regulations. One of the most promising alternatives to traditional marine fuels is Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG). This blog explores the current status and future prospects of LNG fuel for ships, focusing on the types of LNG-fueled ships and the role of INOXCVA in this evolving landscape.
Current Status of LNG as Marine Fuel
LNG has gained traction in the shipping industry due to its potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional fuels. According to recent reports, LNG can lower emissions by 20% to 30% relative to heavy fuel oil (HFO) and emits almost zero sulfur oxides, making it an attractive option for compliance with stringent regulations such as the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) sulfur cap. As of early 2023, LNG accounted for approximately 1.2% of total marine fuel demand, a figure projected to rise to 5.6% by 2030 and further increase to 15.6% by 2050.
The growth in LNG adoption is reflected in the expanding fleet of LNG-fueled vessels. Currently, there are around 251 operational LNG-fueled ships globally, with an additional three percent classified as LNG-ready. The types of LNG-fueled ships include large container vessels, tankers, bulk carriers, and specialized vessels like ferries and tugboats. Major shipping companies are increasingly incorporating dual-fuel engines that can switch between LNG and conventional fuels, enhancing flexibility and operational efficiency.
Types of LNG-Fueled Ships
LNG is being utilized across various segments of the maritime industry. The following are some key types of LNG-fueled ships:
Container Ships: These vessels are among the largest users of LNG as a marine fuel.
Tankers: Both crude oil and chemical tankers are adopting LNG technology, reflecting its versatility across different shipping sectors.
Ferries and Tugboats: These vessels are also transitioning to LNG, benefiting from its cleaner combustion properties.
The versatility of LNG-fueled ships illustrates the fuel’s potential to revolutionize marine transportation while adhering to environmental standards.
Future Prospects for LNG Marine Fuel
The future outlook for LNG as a marine fuel appears promising. The demand for cleaner fuels is expected to drive further investments in LNG infrastructure and technology. With over 30% of new ship orders being either LNG-capable or ready, the trend is likely to continue as shipowners seek compliance with evolving regulations. Moreover, advancements in bunkering infrastructure are crucial for supporting this growth. Significant developments are underway in regions like Asia and the Middle East, where numerous onshore facilities and bunkering vessels are being planned.
However, challenges remain. The volatility in LNG prices compared to traditional fuels poses a risk for ship operators considering the switch to LNG. Additionally, while the number of LNG-capable vessels is increasing, they still represent a small fraction of the overall fleet. As such, achieving cost competitiveness will be essential for broader adoption.
INOXCVA: Leading the Charge in Cryogenic Solutions
As a prominent manufacturer of cryogenic equipment, INOXCVA plays a crucial role in supporting the growth of LNG as a marine fuel. With over 30 years of experience in design, engineering, manufacturing, and installation of cryogenic systems, INOXCVA has positioned itself as a leader in this field. The company offers a comprehensive range of LNG Marine Fuel tanks, engineered with advanced vacuum insulation technology that minimizes boil-off rates—an essential feature for long-haul operations.
INOXCVA’s LNG Marine Fuel tanks come in various configurations and capacities (from 5 m³ to 1250 m³), ensuring adaptability for different vessel designs. Their commitment to safety and compliance with international standards makes them a trusted partner for shipbuilders looking to integrate LNG solutions into their fleets.
Conclusion
The current status and future prospects of LNG as a marine fuel indicate a significant shift towards cleaner energy sources within the shipping industry. The variety of LNG-fueled ships, combined with advancements in infrastructure and technology from companies like INOXCVA, highlights the momentum behind this transition. While challenges such as price volatility exist, the overall trajectory suggests that LNG will play an increasingly vital role in maritime transportation’s sustainable future.
As we look ahead, the integration of LNG Marine Fuel tanks into more vessels will not only enhance environmental performance but also drive innovation within the industry, paving the way for a greener maritime sector that meets both regulatory demands and market expectations.