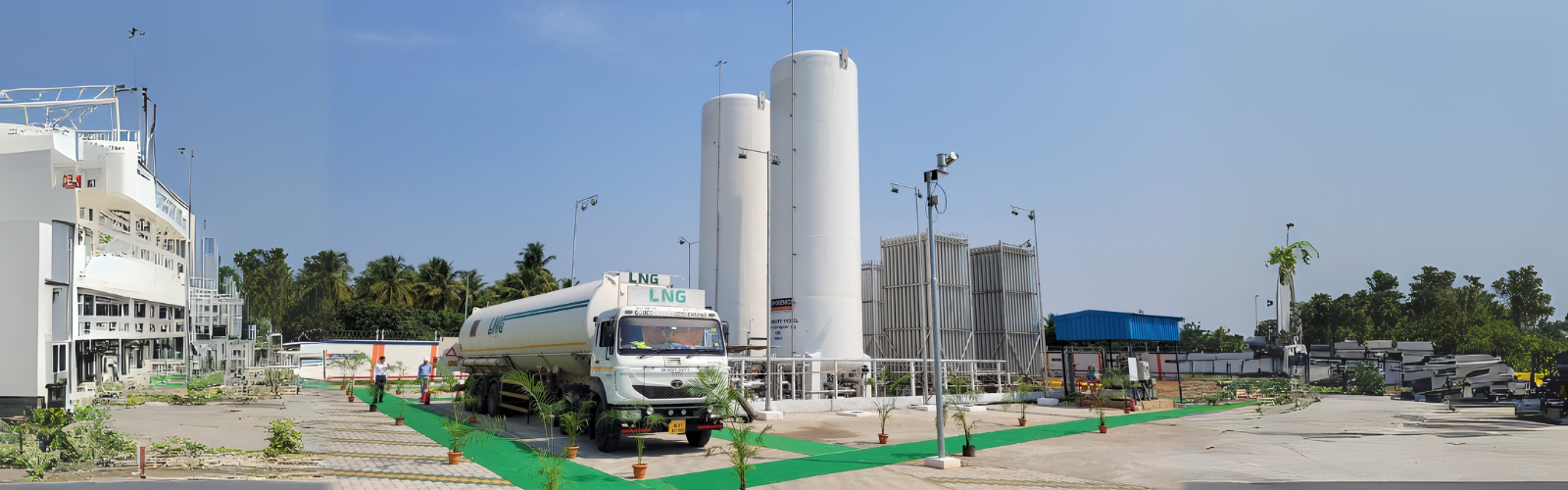
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) has become an essential component of the global energy landscape, offering a cleaner alternative to traditional fossil fuels. The process of converting LNG back to its gaseous state, known as LNG regasification, is crucial for utilising this energy source effectively. In this blog, we will explore how LNG regasification works, its significance in the energy sector, and the role of LNG fuelling stations in this process.
What is LNG Regasification?
LNG regasification is the process of converting liquefied natural gas, which is stored at extremely low temperatures (around -162°C or -260°F), back into its gaseous form. This transformation is necessary to make LNG usable for various applications, including heating, electricity generation, and as a fuel for vehicles. The LNG fuelling stations play a pivotal role in this process by providing the infrastructure needed to distribute the gas to end-users.
The LNG Regasification Process
The LNG regasification process consists of several key stages:
- Storage and Transportation: LNG is transported in specialised cryogenic tanks designed to maintain low temperatures. During transportation, it remains in liquid form until it reaches the regasification terminal.
- Unloading: Upon arrival at the regasification terminal, LNG carriers unload their cargo into insulated storage tanks. This unloading process is critical to ensure that the LNG remains at low temperatures.
- Heating: To convert LNG back into gas, it must be heated. This can be achieved through various methods:
- Open Rack Vaporisers (ORV): These utilise seawater or ambient air to provide the necessary heat.
- Submerged Combustion Vaporisers (SCV): These use a flame submerged in water to heat and vaporise the LNG.
- Heat Exchangers: These devices transfer heat from a hot medium (like seawater) to the cold LNG.
- Pressure Regulation: After heating, the gaseous natural gas must be regulated to ensure it meets the pressure requirements for distribution through pipelines.
- Distribution: Finally, the regasified natural gas is distributed via pipelines or transported further by trucks or smaller ships to reach consumers.
The Role of LNG Fuelling Stations
LNG fuelling stations are critical components of the LNG supply chain. They are designed to receive regasified natural gas and distribute it for various uses, including powering vehicles and supplying energy to industries. These stations ensure that natural gas is available where it is needed most, supporting a transition towards cleaner energy sources.
Benefits of LNG Regasification
The benefits of LNG regasification extend beyond simply converting LNG back into gas:
- Environmental Impact: Natural gas produces fewer emissions compared to coal and oil when burned for energy. By facilitating the use of natural gas through effective regasification processes, we can reduce our overall carbon footprint.
- Energy Security: The ability to import and regasify LNG provides countries with greater energy security by diversifying their energy sources.
- Economic Advantages: Utilising LNG can lead to lower energy costs for consumers and businesses alike, promoting economic growth.
Challenges in Regasification
Despite its advantages, LNG regasification faces several challenges:
- Infrastructure Costs: Building and maintaining regasification terminals and fuelling stations can be expensive.
- Safety Concerns: As LNG is highly flammable, ensuring safety during transportation and regasification is paramount.
- Environmental Considerations: While natural gas is cleaner than other fossil fuels, environmental impacts from regasification processes should be carefully managed.
Conclusion
Understanding how LNG regasification works is vital for grasping its role in today’s energy landscape. The process not only allows for the effective use of liquefied natural gas but also supports cleaner energy initiatives globally. With companies like INOXCVA leading advancements in this field, we can expect continued improvements in efficiency and safety within the LNG fuelling station network.
As we move towards a more sustainable future, embracing technologies that enhance LNG usage will be crucial. The journey from liquid to gas may seem complex, but with robust infrastructure and innovative solutions in place, we can harness the full potential of liquefied natural gas for generations to come.