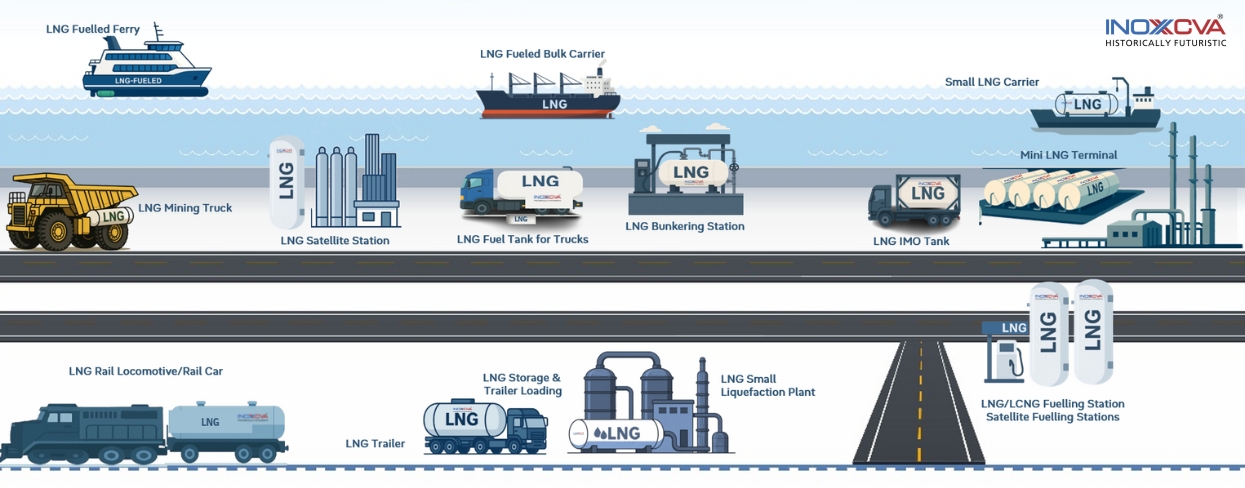
The LNG value chain is a captivating and complex journey that meticulously transforms natural gas into liquefied natural gas (LNG), ultimately delivering this vital energy source to consumers around the globe. This intricate process encompasses several key stages, each demanding cutting-edge technology, precision engineering, and specialized expertise.
It begins with the extraction of natural gas from underground reservoirs, where it is harvested through advanced drilling techniques. The gas is then processed to remove impurities, ensuring that only the highest quality product moves forward.
Stage 1: Extraction and Processing
The journey commences with the careful extraction of natural gas from deep underground reserves, utilizing cutting-edge drilling techniques designed to reach these precious resources efficiently and safely. As the gas is brought to the surface, it undergoes a meticulous processing phase, where advanced facilities work tirelessly to eliminate impurities such as sulfur, water, and carbon dioxide. This crucial purification process ensures that the gas adheres to rigorous quality standards, setting the stage for its transition into the next phase of the liquefied natural gas (LNG) value chain.
Stage 2: Liquefaction
Liquefaction is a critical phase in the transformation of natural gas into liquefied natural gas (LNG). During this process, natural gas is subject to extreme cooling, reaching a frigid temperature of -162°C (-260°F). This dramatic reduction in temperature causes the gas to condense into a liquid, shrinking its volume by approximately 600 times. The result is a compact, manageable form of energy that can be efficiently transported over vast distances, making it a vital component of global energy trade.
The liquefaction process takes place in specialized facilities that are equipped with advanced cryogenic storage tanks and sophisticated cooling systems. These facilities are designed to maintain the ultra-low temperatures required for LNG, ensuring that the gas remains in its liquid state throughout the transportation and storage phases. The careful management of these conditions is crucial for preserving the integrity and quality of LNG, facilitating its journey from production sites to markets around the world.
Stage 3: Transportation
Once liquefied, liquefied natural gas (LNG) is meticulously loaded onto specialized carriers designed specifically for this purpose. These vessels are equipped with advanced cryogenic storage tanks that are meticulously insulated to preserve the LNG’s frigid liquid state throughout its extensive journey across vast oceans or expansive continents. The transportation phase plays a pivotal role in linking production sites, often located in remote areas, with consumer markets situated far and wide. This crucial stage ensures the secure and efficient delivery of LNG, adhering to strict safety standards while navigating potentially challenging maritime conditions.
Stage 4: Storage
Upon arrival at the terminals, liquefied natural gas (LNG) is carefully transferred into large, cryogenically designed storage tanks. These tanks are meticulously engineered to endure the extreme cold necessary to keep LNG in its liquid state, as well as the significant pressures that can arise during the storage process. To prevent any evaporation and ensure the integrity of the LNG, the tanks are equipped with advanced insulation systems. These storage facilities not only serve as a vital buffer but also play a crucial role in maintaining a steady supply of LNG, ensuring its availability during peak demand periods when consumption surges.
Stage 5: Regasification
In the final stage of the liquefied natural gas (LNG) process, regasification transforms LNG back into its gaseous form, enabling it to be utilized effectively. This crucial process involves heating the LNG, which causes it to revert to its original state as natural gas. Regasification plants are strategically positioned close to consumer markets, ensuring that the gaseous product can be delivered promptly and efficiently. The design of these facilities incorporates advanced technologies that optimize energy use and minimize environmental impact, facilitating a seamless transition from liquefied to gaseous energy. This ensures a reliable supply for both residential use and industrial applications, meeting the demands of consumers while promoting energy security.
LNG Distribution: Trailers and Mini-Terminals
After regasification, the journey of LNG continues with efficient distribution to meet diverse energy needs. Not all locations have access to pipelines, which is where reliable transportation and local supply solutions become essential.
INOXCVA’s LNG Semi-Trailers are designed for the safe and efficient movement of LNG over roads. With decades of experience in cryogenic equipment, these trailers provide high-performance transport tailored to various operational needs. They ensure LNG reaches even remote areas, supporting industries and utilities with dependable fuel delivery.
For decentralised supply, Mini-LNG terminals offer a compact and flexible solution. INOXCVA engineers and commissions these terminals to handle LNG import, storage, regasification, and loading for trailers or railcars. Equipped with cryogenic tanks, pumps, and vaporizers, these terminals ensure smooth and safe operations, allowing LNG to be distributed where larger infrastructure isn’t feasible.
Together, LNG trailers and Mini-LNG terminals form an integral part of the LNG value chain, bridging the gap between large-scale production and end-users, and enabling cleaner energy to reach a wider market efficiently.
Conclusion
The liquefied natural gas (LNG) value chain is a remarkable achievement in modern engineering and logistics, intricately designed to ensure the seamless flow of energy from its source to end users. Each stage, from the initial extraction of natural gas from deep underground reservoirs to its transformation into a liquid state for transportation, involves sophisticated technologies and methods. Key components, such as state-of-the-art cryogenic storage tanks, play a critical role in maintaining the gas at ultra-low temperatures to preserve its quality and facilitate efficient transport.
As the LNG travels across oceans and lands, advanced regasification facilities convert it back into gaseous form, ready for distribution. This intricate process not only highlights the significant engineering prowess involved but also emphasizes the strategic importance of LNG in addressing global energy demands in a sustainable manner. By delving into the complexities of the LNG value chain, we gain a deeper appreciation for how this resource is essential in meeting contemporary energy needs while minimizing environmental impacts.