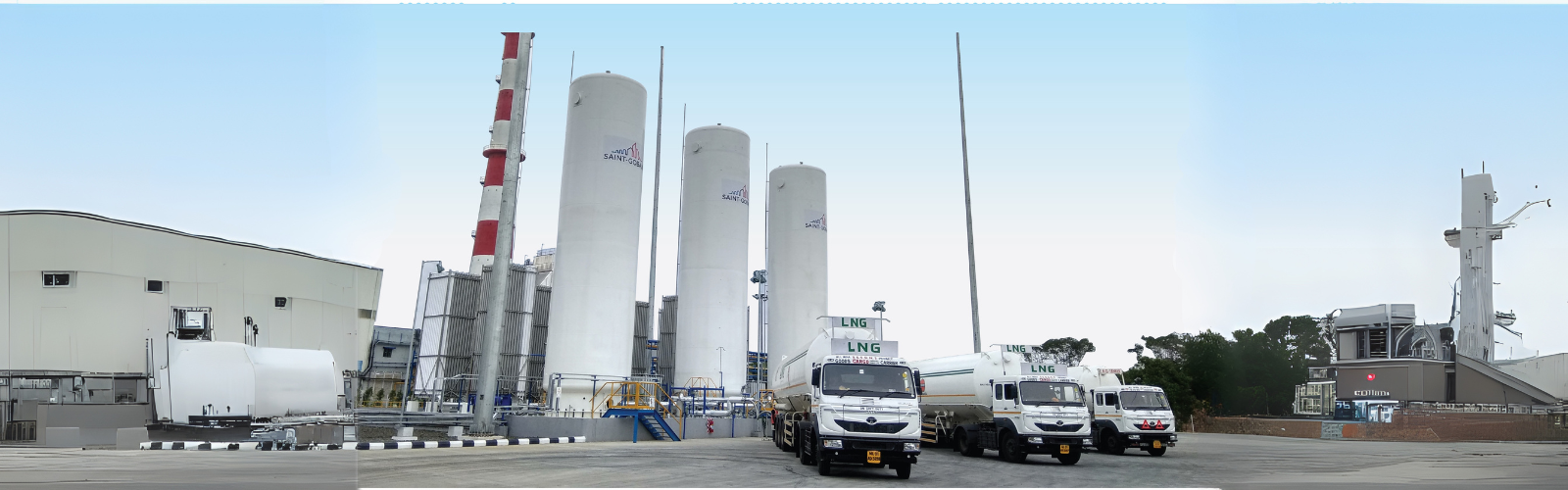
Cryogenics might sound like something straight out of a sci-fi movie, but in reality, it plays an integral role in numerous industrial processes today. From enabling the storage and transportation of gases at incredibly low temperatures to supporting advancements in clean energy, cryogenics is driving industries toward new levels of efficiency and precision. But what exactly is cryogenics storage, and what are the applications of cryogenics in modern industries? Let’s dive deeper into what cryogenic storage is and explore how INOXCVA has become a global leader in cryogenic solutions.
What Is Cryogenics Storage?
At its core, cryogenics refers to the science of producing, storing, and using materials at extremely low temperatures, typically ranging from 2 to 200 Kelvin (-271°C to -73°C). Cryogenics storage involves storing materials, specifically liquefied gases or cryogens, that must remain stable at very cold temperatures. These cryogens include substances like Helium, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon, CO2, N2O, LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas), and Ethylene.
Due to their volatile nature at room temperature, these gases must be stored and transported under special conditions. Cryogenics storage systems are engineered to maintain these ultra-low temperatures, preventing any loss or leakage of valuable gases. This is especially crucial in industries where the precise management of gases is necessary for operational success.
Understanding the Role of Cryogenics and Its Industrial Applications
Cryogenics, the science of achieving and maintaining very low temperatures, is transforming modern industries through innovations in storage, cooling, and material preservation. What is cryogenic storage? Simply put, it refers to the preservation of materials at temperatures below -150°C, where molecular activity slows down considerably, thus preventing degradation over time. This technique is invaluable for sectors requiring long-term stability and safety, including healthcare, pharmaceuticals, environmental science, and electronics.
Applications of Cryogenics in Industry
The applications of cryogenics span across various industries, offering solutions for efficiency, safety, and sustainability. Let’s take a closer look at the key sectors where cryogenics is revolutionizing processes:
Medical and Healthcare: In the medical field, cryogenics is vital for the storage of biological samples such as blood, organs, and stem cells through cryopreservation. This ensures the viability of these samples for future use, often playing a role in life-saving treatments. Additionally, cryogenics powers MRI machines, where liquid helium is used to cool magnets that provide detailed body imaging.
Energy and Clean Fuels: Cryogenics plays a major role in the energy sector, particularly in the storage and transportation of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG), a cleaner fuel alternative. At ultra-low temperatures, natural gas becomes a liquid, making it easier to store and transport in large quantities. This helps reduce carbon emissions globally and enhances energy efficiency. Additionally, cryogenics supports the storage of liquid hydrogen, a key player in renewable energy, and plays a crucial role in fusion energy development.
Food and Beverage Industry: In food processing, cryogenics is used for flash-freezing perishable items such as vegetables, meat, and seafood. Liquid nitrogen helps preserve nutritional value and extends the shelf life of these products. The use of cryogenics in the food industry has revolutionized the way frozen foods are processed and stored, ensuring both quality and safety.
Manufacturing and Metalworking: In manufacturing, cryogenics is employed in processes such as cryogenic hardening and metal treatment. This enhances the strength and durability of metal components, which are crucial in industries like aerospace and automotive. Cryogenics is also pivotal in the creation of superconductors and semiconductors, which are essential for modern electronics and technological innovation.
Space Exploration: Cryogenics is a critical technology in aerospace, especially in space exploration. Rocket fuels like liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen are stored at incredibly low temperatures, and cryogenic storage systems ensure these fuels are safely handled. Without cryogenic technology, the efficient storage and utilization of rocket fuel wouldn’t be possible, making it essential for space missions.
Pharmaceuticals: Cryogenics supports the pharmaceutical industry by ensuring the stability of sensitive biological and chemical compounds during transportation and storage. Many vaccines, enzymes, and other pharmaceutical compounds require cryogenic temperatures to maintain potency and efficacy. This ensures that they remain viable through transportation, storage, and distribution to healthcare facilities, directly impacting patient safety and healthcare outcomes.
Cryosurgery and Cryotherapy: Cryogenics has applications in medical treatments such as cryosurgery and cryotherapy. Cryosurgery uses extreme cold to destroy abnormal or diseased tissues, including warts, tumors, and some cancers. Cryotherapy, on the other hand, involves exposing the body to very low temperatures to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and promote muscle recovery. These treatments have found applications in both clinical and wellness contexts, expanding the reach of cryogenic applications into personalized healthcare.
Electronics and Computing: Cryogenic cooling is instrumental in the electronics and computing industry, particularly in the development of high-performance computing and superconducting materials. Superconductors require cryogenic temperatures to exhibit zero electrical resistance, which enables efficient power transmission and processing. Additionally, quantum computing relies on cryogenics to maintain stable environments for qubits, the fundamental units of quantum computers, thus supporting the rapid advancement of computing technology.
Cryogenic Grinding: Cryogenic grinding, or cryomilling, is a process used in the manufacturing of plastic, rubber, and pharmaceutical powders. The process involves cooling materials to very low temperatures with liquid nitrogen, making them brittle and easy to grind into fine powders. Cryogenic grinding is advantageous because it prevents thermal degradation of materials, ensuring high-quality final products and extending shelf life.
Water Treatment and Environmental Science: Cryogenics is emerging as a useful tool in environmental science, especially in water treatment and pollution control. By using cryogenic processes, pollutants can be separated from water and removed efficiently. Additionally, cryogenics assists in removing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from industrial emissions, helping industries meet regulatory standards and reduce environmental impact.
INOXCVA: Pioneers in Cryogenic Equipment
INOXCVA is a global leader in cryogenic technology, specializing in the design, engineering, and manufacturing of vacuum-insulated cryogenic equipment. Their extensive expertise covers the entire temperature range of cryogenics storage (from 2 to 200 Kelvin), and they provide turnkey solutions for industries that require cryogenic technologies.
INOXCVA works with a wide range of cryogens, including Helium, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon, CO2, N2O, LNG, and Ethylene. By offering vacuum-insulated cryogenic tanks and other storage solutions, INOXCVA ensures that these materials are stored safely and efficiently, meeting the most stringent requirements in the market.
Applications of Cryogenics in Clean Energy and Beyond
INOXCVA is particularly well-known for its contributions to the clean energy sector, where cryogenic storage is crucial. Their cryogenic equipment supports the bulk distribution of LNG and liquid hydrogen, helping industries transition to cleaner, more sustainable energy solutions. As global energy demands shift toward reducing carbon emissions, cryogenics and companies like INOXCVA are playing a pivotal role in this transformation.
Moreover, INOXCVA’s innovations in cryogenics storage and handling extend to other sectors, such as healthcare, manufacturing, and space exploration. Their commitment to quality and excellence makes them a key player in pushing the boundaries of cryogenic technology.
Why Cryogenics is the Future
As industries continue to seek greater precision, efficiency, and sustainability, the applications of cryogenics are set to grow. From ensuring the safe storage of medical samples to supporting clean energy solutions, cryogenics is at the heart of industrial advancements. With global leaders like INOXCVA driving innovation, the future of cryogenics storage looks incredibly promising.
By understanding what cryogenics storage is and exploring its diverse applications, industries worldwide are unlocking new opportunities for growth, efficiency, and sustainability. Cryogenics is not just a technological advancement; it is the key to solving many of the modern world’s industrial challenges.